
Portadown businessman avoids jail for sexual assault of teen under his employment
Defence said the defendant 'continues to deny' the charges and bail in the sum of £1,000 was fixed for appeal
A Portadown man has avoided jail after sexually assaulting a 16-year-old shop worker under his employment. -ADVERTISEMENT- Brian Thomas Chapman (58), of Moyallan Road, appeared before Newry Magistrates’ Court on Monday for sentencing on two counts of sexual assault. The prosecution outlined that on September 23, 2020, a 16-year-old student in the employment of Brian Chapman, disclosed to her mother about incidents that had occurred in her workplace. She said Chapman had put his hand on her thigh and the back of her leg. She also disclosed that she had been getting extra money from him and he had been sending her text messages. The allegations were reported to police the next day, September 24. The victim then took part in an interview on October 9, in which she said, when she was alone in Chapman’s office, he placed his hand on her upper thigh and his other hand on her lower back, underneath her trousers. The defendant was arrested and interviewed at Lurgan police station, where he denied the allegations. His phone was seized and an examination was carried out. The first interview of the defendant took place on October 9, during which he admitted to sending a message about wanting the victim to work 24/7, but stated this was a joke. The second interview took place on January 28, 2021, where he admitted to sending the 24/7 message, but denied sending other messages, such as “hope you’re spending the pounds on something special”. Throughout this process, Chapman denied sending the messages and denied any of the sexual assaults alleged by the victim. On the Chapman’s criminal record, the prosecution added that he was convicted of three common assaults on appeal. In terms of commission, these matters pre-dated this case but the conviction occurred during the running of this case and also involved a female working for the defendant. Prosecution continued that the age of the victim was an aggravating feature, arguing there was a “vulnerability” due to the “power-imbalance” between Chapman and the young student working for him. An additional aggravating feature, they said, was that during the course of the defence, part of the defence was that the victim had “manipulated or manufactured” some of the text messages that were sent. A defence lawyer, speaking on the pre-sentence report, noted the author deemed Chapman to be of low risk. He also noted that similar offences were contested in the County Court in respect of another complaint, with the judge substituting indecent assault charges for common assault. He also argued a Sexual Offences Prevention Order (SOPO) was not necessary as the offending was four years ago, there has been no repetition and risk had been addressed. District Judge Eamonn King noted the defendant was convicted on two of four original charges following a contest, which ran over a number of days, with the case adjourned for a pre-sentence report and victim impact statement to be produced. He added the defendant “continues to deny” the charges and seeks to appeal the outcome. District Judge King, on reading the pre-sentence report, noted the defendant “denies ever hugging or touching the individual and he denies any sexual attraction to the victim”, but pointed to a paragraph in the report which stated, “From the available evidence, it’s possible to surmise that he demonstrated risk taking and impulsive behaviour. It appears that he took advantage of his position and power in a bid to meet his sexual needs, given the victim’s young age and the fact that he was her employer”. The report added that this demonstrated “limited victim empathy and responsibility due to his denial of the offences”. On the victim impact statement, District Judge King described her as a young girl getting her first job, with the “world as her oyster”. He continued: “As a result of what she says occurred, that turned on its head. It left her feeling inwardly uncomfortable, anxious and lonely. She cut herself off from her friends. She stopped going out. She didn’t want to go to school.” He also described a “degree of manipulation” in the case, as this was the victim’s first job and there was a power imbalance between her as an employee, and Chapman as the employer. In his sentencing remarks, District Judge King, said: “I’ve taken time to emphasise to the victim in this case that the victim did nothing wrong. The victim did everything right and the victim shouldn’t feel lonely, anxious or isolated. “The victim should feel confident, strong and outgoing.” Owing to the defendant’s ongoing denial of the charges, he added: “My sentencing exercise isn’t the conclusion of the case today, but I will sentence, so that we can move towards the conclusion going forward. “I am satisfied, irrespective of what the pre-sentence report says, that the defendant took advantage of someone, attempted to groom someone and was guilty of the two offences.” On the two counts, Chapman was sentenced to three months in prison, suspended for two years. He was also made subject to a Sexual Offences Prevention Order (SOPO) for five years and placed on the sex offenders’ register for seven years. Following sentencing, District Judge King fixed bail for appeal at £1,000.
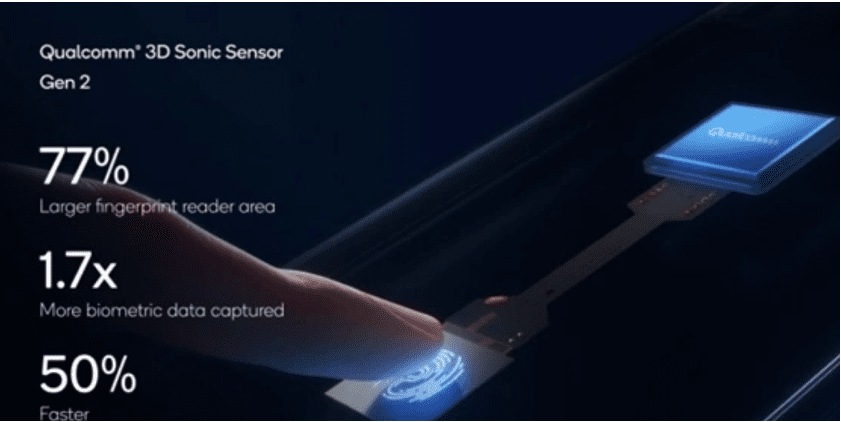
Google Pixel 9 series phones will use Qualcomm ultrasonic fingerprint recognition technology
Google's new generation of flagship smartphone Pixel 9 series is expected to be officially released in mid-August, and the new machine is likely to be equipped with ultrasonic fingerprint recognition technology for the first time to replace the original optical fingerprint recognition. According to core intelligence, Google Pixel 9 series will use the same Qualcomm 3D Sonic Gen 2 ultrasonic fingerprint recognition sensor as the Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra. This ultrasonic technology under the screen fingerprint sensor is Qualcomm released at the CES2021 conference, compared with the previous generation of solutions, the module thickness is further reduced to 0.2mm, while the scanning area is expanded to 8mm×8mm, that is, the recognition area is increased by 77%. This will also allow users to realize fingerprint recognition without having to point their fingertips 100% accurately at the identification area indicated on the screen.
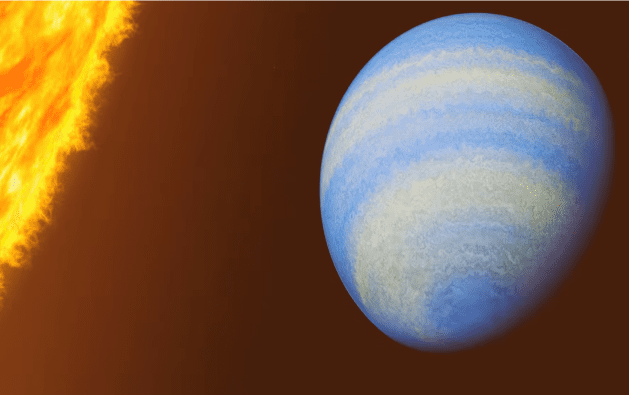
Rotten eggs chemical detected on Jupiter-like alien planet
WASHINGTON, July 8 (Reuters) - The planet known as HD 189733b, discovered in 2005, already had a reputation as a rather extreme place, a scorching hot gas giant a bit larger than Jupiter that is a striking cobalt blue color and has molten glass rain that blows sideways in its fierce atmospheric winds. So how can you top that? Add hydrogen sulfide, the chemical compound behind the stench of rotten eggs. Researchers said on Monday new data from the James Webb Space Telescope is giving a fuller picture of HD 189733b, already among the most thoroughly studied exoplanets, as planets beyond our solar system are called. A trace amount of hydrogen sulfide was detected in its atmosphere, a first for any exoplanet. "Yes, the stinky smell would certainly add to its already infamous reputation. This is not a planet we humans want to visit, but a valuable target for furthering our understanding of planetary science," said astrophysicist Guangwei Fu of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, lead author of the study published in the journal Nature, opens new tab. It is a type called a "hot Jupiter" - gas giants similar to the largest planet in our solar system, only much hotter owing to their close proximity to their host stars. This planet orbits 170 times closer to its host star than Jupiter does to the sun. It completes one orbit every two days as opposed to the 12 years Jupiter takes for one orbit of the sun. In fact, its orbit is 13 times nearer to its host star than our innermost planet Mercury is to the sun, leaving the temperature on the side of the planet facing the star at about 1,700 degrees Fahrenheit (930 degrees Celsius). "They are quite rare," Fu said of hot Jupiters. "About less than one in 100 star systems have them." This planet is located 64 light-years from Earth, considered in our neighborhood within the Milky Way galaxy, in the constellation Vulpecula. A light-year is the distance light travels in a year, 5.9 trillion miles (9.5 trillion km). "The close distance makes it bright and easy for detailed studies. For example, the hydrogen sulfide detection reported here would be much more challenging to make on other faraway planets," Fu said. The star it orbits is smaller and cooler than the sun, and only about a third as luminous. That star is part of a binary system, meaning it is gravitationally bound to another star. Webb, which became operational in 2022, observes a wider wavelength range than earlier space telescopes, allowing for more thorough examinations of exoplanet atmospheres.

Turkey has cancelled a 40 percent tariff on Chinese cars, and BYD has invested $1 billion to build a factory
Byd has grown rapidly in China over the past few years, becoming the country's best-selling car brand and the world's biggest selling electric car brand. Byd opened its first electric car factory in Southeast Asia on Thursday in Thailand. Byd also took over a former Ford Motor Co. plant in Brazil and has been looking for a site for a Mexican plant. Europe's first automotive plant is under construction in Hungary. Byd's second-quarter sales jumped to a record 982,747 vehicles, up more than 40 per cent from a year earlier. Although the company's sales in Europe have been sluggish so far, it is making a big marketing push in the region to replace Volkswagen as the main automotive sponsor of the European Championship. According to a recent Fortune report, officials said that Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan is expected to announce the agreement for BYD to build the plant at a signing ceremony on Monday in Manisa province, where the plant will be built. The officials spoke on condition of anonymity because they were not authorized to speak publicly. Byd representatives declined to comment. Turkish Industry and Technology Minister Mohamed Fatih Kassir said in May that he was in advanced discussions with BYD and Chery on investment in Turkey. The new plant will improve BYD's access to the European Union, as Turkey has a customs union agreement with the EU. The European Union this week announced temporary punitive tariffs on electric vehicles imported from China, with BYD imposing an additional 17.4 percent tariff on top of the existing 10 percent tariff. Other Chinese carmakers have been hit with higher tariffs. Investing in Turkey would strengthen the presence of Chinese carmakers in Europe at a time of escalating trade tensions.

Audi RS e-tron GT intelligent cockpit innovation analysis
RS e-tron GT: Shares J1 platform with Porsche Taycan. The iconic closed hexagonal "big mouth" is quite a brand recognition, and the rear of the car uses a decorative design shaped like a diffuser. Although the difference between it and the regular e-tron GT is very limited, the "RS" nameplate on the rear of the car means that it is not an ordinary person, of course, low-key is also the style of AUD-Sport. The center console continues the family design of the Audi brand, the lines are simple and refined, and the center control screen, the front air conditioning control panel and the function keys below are obviously tilted to the driver's side, echoing the product positioning of the driver's car. Sports seats, leather fabrics with red stitches, etc. appear in the configuration table of the car, rendering the interior sports atmosphere just right, and the overall beauty of the cabin has been affirmed by the reviewers. Although the official model of the cockpit chip selected by the car has not been announced, it has a high score in the evaluation items such as the cold start speed of the car, the start speed of the core application and the navigation search speed, which shows that the car performance is good. In addition, in terms of specifications and accuracy, the car received full marks in the touch accuracy and screen sharpness evaluation, and the daily high-frequency interaction experience is excellent. Of course, if you optimize the voice car control ability, its intelligent experience will be a higher level.





