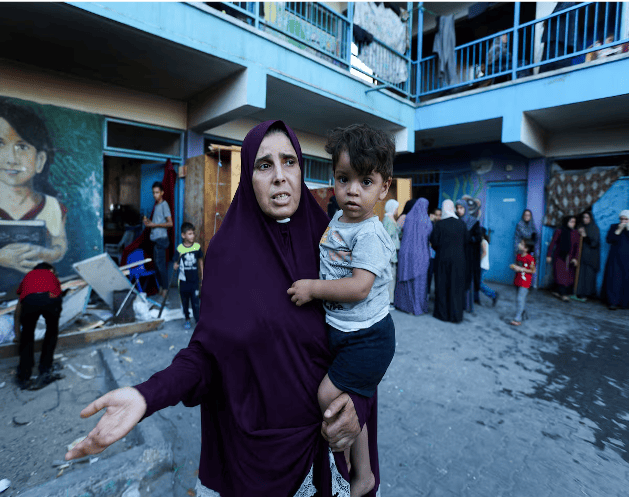Carlsberg to buy Britvic for $4.2 billion
Carlsberg to buy Britvic for 1,315p per share Carlsberg will also buy out Marston's from brewing joint venture Danish brewer plans to create integrated beverage business in UK Shares in Carlsberg, Britvic, Marston's all rise July 8 (Reuters) - Carlsberg (CARLb.CO), opens new tab has agreed to buy British soft drinks maker Britvic (BVIC.L), opens new tab for 3.3 billion pounds ($4.23 billion), a move the Danish brewer said would forge a UK beverage "powerhouse" and that sent both companies' shares higher. Carlsberg clinched the takeover with a sweetened bid of 1,315 pence per share - comprising cash and a special dividend of 25 pence a share - after the British company rejected 1,250 pence per share last month. The acquisition will create value for shareholders, contribute to growth and forge a combined beer and soft drink company that is unique in the UK, CEO Jacob Aarup-Andersen told investors on a conference call. "With this transaction we are creating a UK powerhouse," he said. He brushed off concerns from some analysts about integration risks, saying Carlsberg has a strong track record of running beer and soft drink businesses in several markets. Soft drinks already make up 16% of Carlsberg's volumes. COST SAVINGS As drinkers in some markets ditch beer for spirits or cut back on drinking altogether, brewers have looked to broaden their portfolio into new categories like hard seltzer, canned cocktails and cider, as well as zero-alcohol brews. Britvic sells non-alcoholic drinks in Britain, Ireland, Brazil and other international markets such as France, the Middle East and Asia. Carlsberg said the deal will deliver a number of benefits, including cost and efficiency savings worth 100 million pounds ($128 million) over five years as it takes advantage of common procurement, production and distribution networks. It will also see Carlsberg take over Britvic's bottling agreement with PepsiCo (PEP.O), opens new tab. Carlsberg already bottles PepsiCo drinks in several markets and there is scope to add more geographies in future, Aarup-Andersen said. arlsberg halted share buy backs on Monday as a result of the deal. Chief financial officer Ulrica Fearn said these would resume once Carlsberg reaches its revised target for net debt of 2.5 times EBITDA, from 3.5 times currently - a goal it expects to meet in 2027. "Whilst this represents a shift in the strategy away from organic top- and bottom-line growth and consistent returns to shareholders, we view it as a relatively low risk transaction with attractive financials," Jefferies analysts said in a note. Carlsberg also said on Monday it will buy out UK pub group Marston's (MARS.L), opens new tab from a joint venture for 206 million pounds. That will give it full ownership of the newly formed Carlsberg Britvic after the deal. ($1 = 0.7805 pounds) Get the latest news and expert analysis about the state of the global economy with Reuters Econ World. Sign up here. Reporting by Stine Jacobsen, Yadarisa Shabong and Emma Rumney Editing by Sherry Jacob-Phillips, Rashmi Aich, David Goodman and David Evans

Turkey has cancelled a 40 percent tariff on Chinese cars, and BYD has invested $1 billion to build a factory
Byd has grown rapidly in China over the past few years, becoming the country's best-selling car brand and the world's biggest selling electric car brand. Byd opened its first electric car factory in Southeast Asia on Thursday in Thailand. Byd also took over a former Ford Motor Co. plant in Brazil and has been looking for a site for a Mexican plant. Europe's first automotive plant is under construction in Hungary. Byd's second-quarter sales jumped to a record 982,747 vehicles, up more than 40 per cent from a year earlier. Although the company's sales in Europe have been sluggish so far, it is making a big marketing push in the region to replace Volkswagen as the main automotive sponsor of the European Championship. According to a recent Fortune report, officials said that Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan is expected to announce the agreement for BYD to build the plant at a signing ceremony on Monday in Manisa province, where the plant will be built. The officials spoke on condition of anonymity because they were not authorized to speak publicly. Byd representatives declined to comment. Turkish Industry and Technology Minister Mohamed Fatih Kassir said in May that he was in advanced discussions with BYD and Chery on investment in Turkey. The new plant will improve BYD's access to the European Union, as Turkey has a customs union agreement with the EU. The European Union this week announced temporary punitive tariffs on electric vehicles imported from China, with BYD imposing an additional 17.4 percent tariff on top of the existing 10 percent tariff. Other Chinese carmakers have been hit with higher tariffs. Investing in Turkey would strengthen the presence of Chinese carmakers in Europe at a time of escalating trade tensions.

BRI: embracing Chinese green practices for a sustainable future
Editor's Note: This year marks the 10th anniversary of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) proposed by Chinese President Xi Jinping. Through the lens of foreign pundits, we take a look at 10 years of the BRI - how it achieves win-win cooperation between China and participating countries of the BRI and how it has given the people of these countries a sense of fulfillment. In an interview with Global Times (GT) reporter Li Aixin, Erik Solheim (Solheim), former under-secretary-general of the United Nations and former executive director of the UN Environment Programme, recalled how the BRI helped shorten a previously long journey in Sri Lanka to a half-hour trip. "We will all be losers in a de-globalized, de-coupled world. The BRI can play a key role in bringing the world together," Solheim said. This is the 18th piece of the series. GT: How do you evaluate the role of the BRI in promoting development in participating countries over the past 10 years? Solheim: The BRI has been a major driver of development since it was announced by President Xi Jinping in Kazakhstan 10 years ago. The China-Laos Railway has connected landlocked Laos to the Chinese and European rail network, making it possible for Laos to sell more goods and welcome more tourists. Rail corridors in Kenya and from Djibouti to Addis Ababa connect the interior of Africa to the coast, bringing opportunities for much faster development in East Africa. The Bandung-Jakarta railway in Indonesia, Hanoi metro, roads and ports in Sri Lanka - there are great examples of good south-south and BRI projects in almost every corner of the world. GT: In your experience of traveling around the world, has any BRI-related story left a deep impression on you? Solheim: Yes, many! I'll just mention two. When I was chief negotiator in the Sri Lanka peace process 15 years ago, it took a long time to travel from the airport to Colombo, the capital of Sri Lanka. When I came back last year, it took half an hour on wonderful Chinese-built highways. Traveling through Mombasa, a coastal city in Kenya, you see a lot of poverty and run down houses. Then all of a sudden, a green, clean, well-run oasis opens up. It's the end station of the Nairobi-Mombasa railway which links the capital Nairobi to the coast. The rail station stands out and is showing the future for Kenya. GT: The EU proposed the Global Gateway, and the US proposed the Build Back Better World. What do you think are the similarities and differences between these projects and the BRI? Solheim: I really wish success for the Western initiatives. What developing nations ask for is a choice of good cooperation with both China and the West. Unfortunately, up to now, a number of the Western-led initiatives have been more like media events. They lack structure, secretariat, finances and clear direction. Nearly all nations in the world want to see close people-to-people relations, investment and political cooperation with both China and the West. No one wants to choose. GT: Some people from the West are talking about "de-coupling" and "de-risking." Both seem to be another way of saying "de-globalization." Do you think "de-coupling" and "de-risking" will affect the BRI? And what role will the BRI play in maintaining globalization? Solheim: Decoupling is probably the most unwise idea in the world today. It's outright dangerous. Facing climate change, environmental degradation, economic troubles, war in Ukraine and other places, and the threat of pandemics, we need more, not less, cooperation. We will all be losers in a de-globalized, de-coupled world. The BRI can play a key role in bringing the world together. Almost all developing countries have made BRI agreements with China. As an example, when President Xi met all the leaders of Central Asia recently in Xi'an, Northwest China's Shaanxi Province, they made a very ambitious declaration on future green cooperation between China and Central Asia. GT: You have previously said that the BRI is a fantastic vehicle to promote green global development, which can boost the economy and ecology at the same time. Could you elaborate on how you think the BRI has achieved development of the economy and ecology? Solheim: In the beginning there were too many fossil fuel projects among BRI programs. In the BRI International Green Development Coalition, we argued this should stop. When President Xi pledged to stop building new coal-fired power projects overseas, it was one of the most important environmental decisions ever. Also, it happened at a time when important BRI nations like Bangladesh, Kenya and Pakistan decided they could grow their economies and go green without coal. The BRI will in the next decade become the world's most important vehicle for green energy and green transport. We will see massive investments in solar and wind power, hydrogen, electric batteries and more. GT: How do you view China's goal of achieving harmony between humanity and nature in modernization? In what way is China's story in pursuing harmony between humanity and nature relevant to other countries? Solheim: China now covers between 60 percent and 80 percent of all major green technologies in the world - solar, wind, hydro, batteries, electric cars and high-speed rail. Companies like Longi, BYD and CATL are the world leaders in their sectors. More remarkably and maybe less noticed abroad, China is also a global leader in protecting nature. It's embarking upon one of the most massive national park programs, with a focus on Qinghai Province and Xizang Autonomous Region. China is by far the biggest tree planter in the world and the global leader in desert control in Kubuqi, Inner Mongolia and other places. China has been hugely successful in the recovery of endangered species like the Giant Panda, Tibetan Antelope and Snow Leopard. A new center for mangrove restoration is being set up in Shenzhen and the fishing ban in the Yangtze will restore that magnificent ecosystem. The Belt and Road is a great opportunity for the world to learn from good Chinese green practices.
Israeli strike kills 16 at Gaza school, military says it targeted gunmen
CAIRO/GAZA, July 6 (Reuters) - At least 16 people were killed in an Israeli strike on a school sheltering displaced Palestinian families in central Gaza on Saturday, the Palestinian health ministry said, in an attack Israel said had targeted militants. The health ministry said the attack on the school in Al-Nuseirat killed at least 16 people and wounded more than 50. The Israeli military said it took precautions to minimize risk to civilians before it targeted the gunmen who were using the area as a hideout to plan and carry out attacks against soldiers. Hamas denied its fighters were there. At the scene, Ayman al-Atouneh said he saw children among the dead. "We came here running to see the targeted area, we saw bodies of children, in pieces, this is a playground, there was a trampoline here, there were swing-sets, and vendors," he said. Mahmoud Basal, spokesman of the Gaza Civil Emergency Service, said in a statement that the number of dead could rise because many of the wounded were in critical condition. The attack meant no place in the enclave was safe for families who leave their houses to seek shelters, he said. Al-Nuseirat, one of Gaza Strip's eight historic refugee camps, was the site of stepped-up Israeli bombardment on Saturday. An air strike earlier on a house in the camp killed at least 10 people and wounded many others, according to medics. In its daily update of people killed in the nearly nine-month-old war, the Gaza health ministry said Israeli military strikes across the enclave killed at least 29 Palestinians in the past 24 hours and wounded 100 others.

Samsung hit the biggest strike! Over 6,500 people attended.
More than 6,500 employees at South Korea's Samsung Electronics began a three-day mass strike on Monday (July 8), demanding an extra day of paid annual leave, higher pay raises and changes to the way performance bonuses are currently calculated. This is the largest organized strike in Samsung Electronics' more than half century of existence, and the union said that if this strike does not push employees' demands to be met, a new strike may be called. One of the core issues of the current dispute between the labor union and Samsung Electronics is raising wages and increasing the number of paid vacation days. The second demand is a pay rise. The union originally wanted a pay rise of more than 3% for its 855 employees, but last week they changed their demand to include all employees (rather than just 855). The third issue involves performance bonuses linked to Samsung's outsized profits - chip workers did not receive the bonuses last year when Samsung lost about Won15tn and, according to unions, fear they will still not get the money even if the company manages to turn around this year.