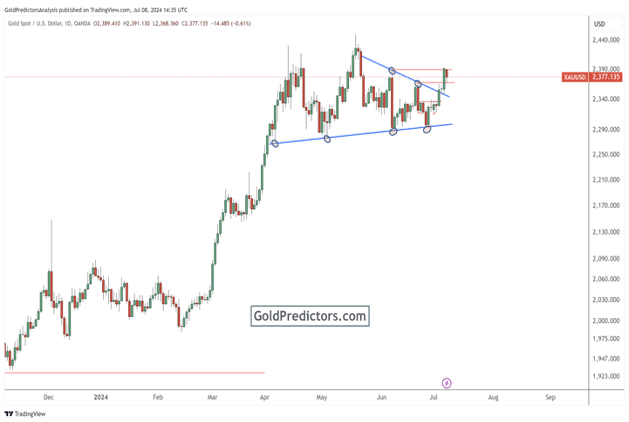
Gold reaction to employment data and geopolitical events
The June US Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) data showed an increase of 206,000 jobs, exceeding expectations. Political uncertainty and the People's Bank of China's pause in gold purchases influence gold market dynamics. Recent technical developments in the gold market, including breaking the triangle formation and subsequent rally, indicate the potential for higher prices. Despite a bullish outlook, further consolidation is possible before a significant surge. The recent US Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) data revealed a rise of 206,000 jobs in June, surpassing the market expectation of 190,000, despite a downward revision from 272,000 to 218,000 for May. The unemployment rate increased to 4.1% and the wage inflation declined to 3.9% year-over-year. These mixed employment signals have increased the likelihood of a rate cut by the Federal Reserve in September. Additionally, political developments in France, where the left-wing New Popular Front led by Jean-Luc Mélenchon is poised to win a significant number of seats, add to the global economic uncertainty. Meanwhile, the People's Bank of China (PBoC) has paused its gold purchasing program, potentially waiting for a further price pullback. These factors collectively influence gold prices, providing a complex backdrop where the prospect of lower interest rates, political uncertainty, and central bank purchasing strategies are likely to drive market dynamics and investor behaviour in the coming months. Bullish Trends in Gold Prices The announcement of the NFP data has dropped the US Dollar Index and boosted gold prices. Since the gold market broke the triangle formation on Wednesday and formed an inside candle on Thursday, the break above Thursday's high on Friday initiated a strong rally, closing the price at higher levels. The red line was the first resistance of this breakout where the gold closed the last week. A clear break above this level may initiate another surge higher. The breakout of the triangle suggests higher prices, but the risk environment remains, as June was a correction month. It looks like the price is preparing for higher levels, but the possibility of consolidation before the surge cannot be ignored. Bottom line In conclusion, the increase in US employment, despite mixed signals in wage inflation and unemployment, has increased the likelihood of a Federal Reserve rate cut, boosting gold prices while weakening the US Dollar Index. Political uncertainties in France and the pause in gold purchases by the People's Bank of China further contribute to the complex economic landscape, indicating potential volatility ahead. The gold market's recent technical developments, including breaking the triangle formation and the subsequent rally, suggest readiness for higher prices. However, the possibility of consolidation before another significant surge remains, necessitating careful observation by investors as the market navigates these multifaceted influences.
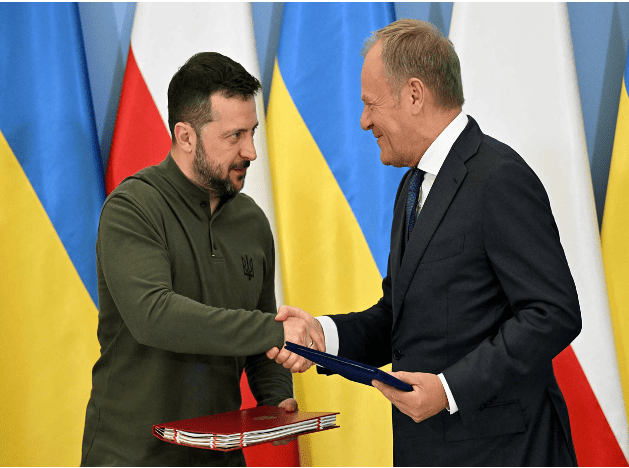
Poland and Ukraine sign bilateral security agreement
On July 8, Ukrainian President Zelensky, who was visiting Poland, and Polish Prime Minister Tusk signed a bilateral security agreement in Warsaw, the capital of Poland. The agreement clearly states that Poland will provide support to Ukraine in air defense, energy security and reconstruction. After signing the agreement, Tusk said that the agreement includes actual bilateral commitments, not "empty promises." Previously, the United States, Britain, France, Germany and other countries as well as the European Union signed similar agreements with Ukraine.

Coexisting and cooperating with China is the only choice for the US
US Secretary of State Antony Blinken declared at the Munich Security Conference: "If you're not at the table in the international system, you're going to be on the menu." The arrogant thinking of American political elites is evident: Whoever does not comply with the US will be excluded from the table of the American-led system and put on the menu. How arrogant. The US is actively pushing for "decoupling" from China and trying to persuade the entire West to "decouple" from China, using the term "de-risking." Washington hopes to ultimately contain China's development in order to maintain American hegemony. However, this time, Washington is facing a historically experienced and strategically rich Eastern civilization. Previous opponents targeted by the US have chosen to confront the US strategically. The US not only has the strongest technological and military capabilities but also controls global financial and information networks with a large number of allies. Those countries that had engaged in direct confrontations had suffered losses. Some of them had disintegrated, some had been weakened, and some had fallen into difficulties. However, what Washington sees from China is strategic composure and resilience. China is now staging an unprecedented and grand "Tai Chi." However, some Chinese people feel that this is not enough: Why can't we confront the US head-on? But I want to say that this is precisely the brilliance of China. This grand "Tai Chi" is about dismantling the pressure the US is putting on China. Europe is different from the US. A European diplomat once said in private that the topic of China has become toxic in the US, but in Europe, it is still possible to openly display friendliness toward China. There is genuine competition between the Europe and China despite Europe leans more toward the US between China and the US. Only in terms of ideology does the term "West" truly exist. In terms of fundamental economic interests, Europe has considerable independence. In terms of security, their attitude toward China also differs greatly from that of the US. In the Asia-Pacific region or China's periphery, the US wants to create an "Asian NATO." The specific situations of countries in dispute with China are very different. China has enormous influence in the region, is the largest trading partner of the vast majority of countries in the region and has friendly relations with most countries in the region. The disputes with countries are not fundamental strategic conflicts, and China has the ability to manage disputes with each specific country and push them to move toward neutrality to varying degrees without being tied to the US' policy toward China. China has a lot of trading partners and stakeholders in the US. The trade volume between China and the US, despite the decline, reached $664.4 billion in 2023, which shows China's huge presence in the US, and is the bond of the two countries in the current situation. The US is not a country where the political elites can have absolute say, and the huge interests have forced the US president and senior officials to repeatedly proclaim that they "don't want to decouple from China" and instead they want to "manage the US-China competition" and see "preventing a war with China" as clearly in everyone's best interest. China should engage in a "strategic battle" with the US at the closest possible distance. We need to maintain friendly relations with certain forces within the US, speed up the resumption of flights between the two countries, increase personnel exchanges and completely reverse the downturn of China-US contacts during the pandemic. In addition to the above dismantling, we also have the huge increment in the "Belt and Road." This initiative will increase China's power to compete with the US, greatly extending the front line that the US needs to maintain in containing China, making the US more powerless. In order to dismantle the US strategy toward China, China must become more diversified while maintaining strategic consistency. Our national diplomacy toward the US is very principled, rational and determined, which is clearly different from other countries targeted by the US. Our public diplomacy toward the US needs to be unique, with both "anti-American voices" and efforts to maintain friendly relations between the two societies and further expand economic and practical cooperation with the US. Just as eagles have their own way of flying and doves have their own formation, just as we see the US as complex, China must also be seen as complex in the eyes of the US. China is both a geopolitical concern and a profitable investment destination for them, and is one of the largest trading partners that is difficult to replace. Some American political elites proclaim China as an "enemy," but it is important to make the majority of Americans feel that China is not. No matter how intense the struggles between China and the US may be, we cannot shape the entire US toward an enemy direction. China has to make the US political elites recognize that it is futile to deal with China in the same way as it historically dealt with the Soviet Union and other major powers. Furthermore, willingly or unwillingly, coexistence and cooperation with China will be their only choice.

Zuckerberg surfed and drank beer on vacation, Musk: I prefer to work
After Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg posted a video on his Facebook and Instagram accounts of his free time during the Independence Day holiday on the X platform, Musk said, "I prefer to work." Zuckerberg posted a video of himself surfing on a hydrofoil in a tuxedo, waving an American flag and drinking a beer, and wrote: "Happy birthday America." The video quickly went viral, and after greg shared it on the X platform, Musk replied: "I hope he continues to have fun on the yacht." I prefer to work." Musk, a workaholic, attended the 29th annual Barron Investment Conference in November 2022, where he said: "My workload went from 78 hours a week to 120 hours a week..." In 2018, he slept on the floor of the Gigafactory in Fremont in an effort to ramp up production of the Tesla Model 3.
Samsung expects profits to jump by more than 1,400%
Samsung Electronics expects its profits for the three months to June 2024 to jump 15-fold compared to the same period last year. An artificial intelligence (AI) boom has lifted the prices of advanced chips, driving up the firm's forecast for the second quarter. The South Korean tech giant is the world's largest maker of memory chips, smartphones and televisions. The announcement pushed Samsung shares up more than 2% during early trading hours in Seoul. The firm also reported a more than 10-fold jump in its profits for the first three months of this year. In this quarter, it said it is expecting its profit to rise to 10.4tn won ($7.54bn; £5.9bn), from 670bn won last year. That surpasses analysts' forecasts of 8.8tn won, according to LSEG SmartEstimate. "Right now we are seeing skyrocketing demand for AI chips in data centers and smartphones," said Marc Einstein, chief analyst at Tokyo-based research and advisory firm ITR Corporation. Optimism about AI is one reason for the broader market rally over the last year, which pushed the S&P 500 and the Nasdaq in the United States to new records on Wednesday. The market value of chip-making giant Nvidia surged past $3tn last month, briefly holding the top spot as the world's most valuable company. "The AI boom which massively boosted Nvidia is also boosting Samsung's earnings and indeed those of the entire sector," Mr Einstein added. Samsung Electronics is the flagship unit of South Korean conglomerate Samsung Group. Next week, the tech company faces a possible three-day strike, which is expected to start on Monday. A union of workers is demanding a more transparent system for bonuses and time off.





