iPhone 16 Pro leak just confirmed a huge camera upgrade
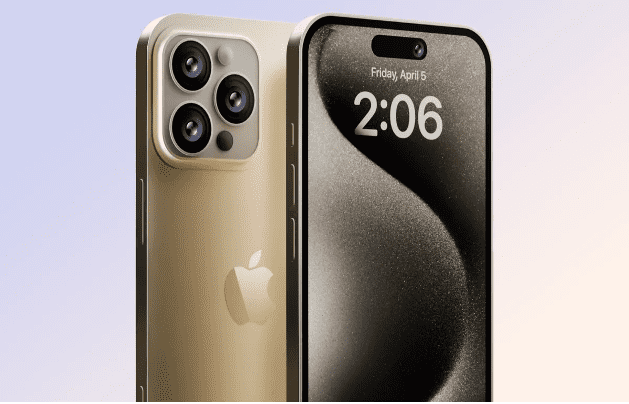
The tetraprism lens with 5x optical zoom currently exclusive to the iPhone 15 Pro Max could be headed to both the iPhone 16 Pro and iPhone 16 Pro Max, narrowing the gap between Apple's premium flagships. That's according to a new report from analyst Ming-Chi Kuo, who cites a recent earnings call with Apple lens supplier Largan. In the call, a spokesperson from Largan said "some flagship specifications will be extended to other models" in the second half of 2024, presumably in reference to the upcoming iPhone Pro models. "Apple is Largan’s largest customer, and Largan is also Apple’s largest lens supplier," Kuo said. "Therefore, the quote likely refers to the fact that the new iPhone 16 Pro and Pro Max will have a tetraprism camera in 2H24 (while only the iPhone 15 Pro Max had this camera in 2H23).” The report goes on to say that the tetraprism camera for the iPhone 16 Pro series won't be all that different from the one in the iPhone 15 Pro Max. While the lack of an upgrade is disappointing, it's not necessarily a bad thing as these kinds of lenses are already top-of-the-line. They represent a major increase over prior models’ zoom capabilities, and they're capable of offering more depth while still fitting into super-slim smartphones. That being said, Apple does appear to be revamping the main camera and ultra-wide camera on the iPhone 16 Pro Max. Evidence continues to mount that both iPhone 16 Pro models will share the same 5x optical zoom camera. Earlier this week, DigitTimes in Asia (via 9to5Mac) reported that Apple is set to ramp up orders for tetraprism lenses as it expands their use in its upcoming iPhone series. Industry sources told the outlet that Largan and Genius Electronic Optical were tapped as the primary suppliers. Apple would be wise to streamline its Pro-level iPhones with the same camera setup; then all customers have to consider with their choice of a new iPhone is the size and price. Of course, this should all be taken with a grain of sand for now until we hear more from Apple. It's still a while yet before Apple's usual September time window for iPhone launches. In the meantime, be sure to check out all the rumors so far in our iPhone 16, iPhone 16 Pro and iPhone 16 Pro Max hubs.

TSX futures rise ahead of Fed chair Powell's testimony
July 9 (Reuters) - Futures linked to Canada's main stock index rose on the back of metal prices on Tuesday, while investors awaited U.S. Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell's congressional testimony on monetary policy later in the day. The S&P/TSX 60 futures were up 0.25% by 06:28 a.m. ET (1028 GMT). The Toronto Stock Exchange's materials sector was set to re Oil futures , dipped as fears over supply disruption eased after Hurricane Beryl, which hit major refineries along with the U.S. Gulf Coast, caused minimal impact. Markets will be heavily focussed on Powell's two-day monetary policy testimony before the Senate Banking Committee, starting at 10 a.m. ET (1400 GMT), which can help investors gauge the Fed's rate-cut path. Following last week's softer jobs data, market participants are now pricing in a 77% chance of a rate cut by the U.S. central bank in September. The main macro event for the markets this week will be the U.S. consumer prices data due on Thursday, which can help assess the trajectory of inflation in the world' biggest economy. Wall Street futures were also up on Tuesday after the S&P 500 (.SPX), opens new tab and Nasdaq (.IXIC), opens new tab touched record closing highs in the previous session. In Canada, fears of the economy slipping into recession advanced after the latest data showed that the unemployment rate rose to a 29-month high in June. Traders are now pricing in a 65% chance of another cut by the Bank of Canada, which already trimmed interest rates last month. In corporate news, Cenovus Energy (CVE.TO), opens new tab said it is demobilizing some staff at its Sunrise oil sands project in northern Alberta as a precaution due to the evolving wildfire situation in the area.

BRI: embracing Chinese green practices for a sustainable future
Editor's Note: This year marks the 10th anniversary of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) proposed by Chinese President Xi Jinping. Through the lens of foreign pundits, we take a look at 10 years of the BRI - how it achieves win-win cooperation between China and participating countries of the BRI and how it has given the people of these countries a sense of fulfillment. In an interview with Global Times (GT) reporter Li Aixin, Erik Solheim (Solheim), former under-secretary-general of the United Nations and former executive director of the UN Environment Programme, recalled how the BRI helped shorten a previously long journey in Sri Lanka to a half-hour trip. "We will all be losers in a de-globalized, de-coupled world. The BRI can play a key role in bringing the world together," Solheim said. This is the 18th piece of the series. GT: How do you evaluate the role of the BRI in promoting development in participating countries over the past 10 years? Solheim: The BRI has been a major driver of development since it was announced by President Xi Jinping in Kazakhstan 10 years ago. The China-Laos Railway has connected landlocked Laos to the Chinese and European rail network, making it possible for Laos to sell more goods and welcome more tourists. Rail corridors in Kenya and from Djibouti to Addis Ababa connect the interior of Africa to the coast, bringing opportunities for much faster development in East Africa. The Bandung-Jakarta railway in Indonesia, Hanoi metro, roads and ports in Sri Lanka - there are great examples of good south-south and BRI projects in almost every corner of the world. GT: In your experience of traveling around the world, has any BRI-related story left a deep impression on you? Solheim: Yes, many! I'll just mention two. When I was chief negotiator in the Sri Lanka peace process 15 years ago, it took a long time to travel from the airport to Colombo, the capital of Sri Lanka. When I came back last year, it took half an hour on wonderful Chinese-built highways. Traveling through Mombasa, a coastal city in Kenya, you see a lot of poverty and run down houses. Then all of a sudden, a green, clean, well-run oasis opens up. It's the end station of the Nairobi-Mombasa railway which links the capital Nairobi to the coast. The rail station stands out and is showing the future for Kenya. GT: The EU proposed the Global Gateway, and the US proposed the Build Back Better World. What do you think are the similarities and differences between these projects and the BRI? Solheim: I really wish success for the Western initiatives. What developing nations ask for is a choice of good cooperation with both China and the West. Unfortunately, up to now, a number of the Western-led initiatives have been more like media events. They lack structure, secretariat, finances and clear direction. Nearly all nations in the world want to see close people-to-people relations, investment and political cooperation with both China and the West. No one wants to choose. GT: Some people from the West are talking about "de-coupling" and "de-risking." Both seem to be another way of saying "de-globalization." Do you think "de-coupling" and "de-risking" will affect the BRI? And what role will the BRI play in maintaining globalization? Solheim: Decoupling is probably the most unwise idea in the world today. It's outright dangerous. Facing climate change, environmental degradation, economic troubles, war in Ukraine and other places, and the threat of pandemics, we need more, not less, cooperation. We will all be losers in a de-globalized, de-coupled world. The BRI can play a key role in bringing the world together. Almost all developing countries have made BRI agreements with China. As an example, when President Xi met all the leaders of Central Asia recently in Xi'an, Northwest China's Shaanxi Province, they made a very ambitious declaration on future green cooperation between China and Central Asia. GT: You have previously said that the BRI is a fantastic vehicle to promote green global development, which can boost the economy and ecology at the same time. Could you elaborate on how you think the BRI has achieved development of the economy and ecology? Solheim: In the beginning there were too many fossil fuel projects among BRI programs. In the BRI International Green Development Coalition, we argued this should stop. When President Xi pledged to stop building new coal-fired power projects overseas, it was one of the most important environmental decisions ever. Also, it happened at a time when important BRI nations like Bangladesh, Kenya and Pakistan decided they could grow their economies and go green without coal. The BRI will in the next decade become the world's most important vehicle for green energy and green transport. We will see massive investments in solar and wind power, hydrogen, electric batteries and more. GT: How do you view China's goal of achieving harmony between humanity and nature in modernization? In what way is China's story in pursuing harmony between humanity and nature relevant to other countries? Solheim: China now covers between 60 percent and 80 percent of all major green technologies in the world - solar, wind, hydro, batteries, electric cars and high-speed rail. Companies like Longi, BYD and CATL are the world leaders in their sectors. More remarkably and maybe less noticed abroad, China is also a global leader in protecting nature. It's embarking upon one of the most massive national park programs, with a focus on Qinghai Province and Xizang Autonomous Region. China is by far the biggest tree planter in the world and the global leader in desert control in Kubuqi, Inner Mongolia and other places. China has been hugely successful in the recovery of endangered species like the Giant Panda, Tibetan Antelope and Snow Leopard. A new center for mangrove restoration is being set up in Shenzhen and the fishing ban in the Yangtze will restore that magnificent ecosystem. The Belt and Road is a great opportunity for the world to learn from good Chinese green practices.
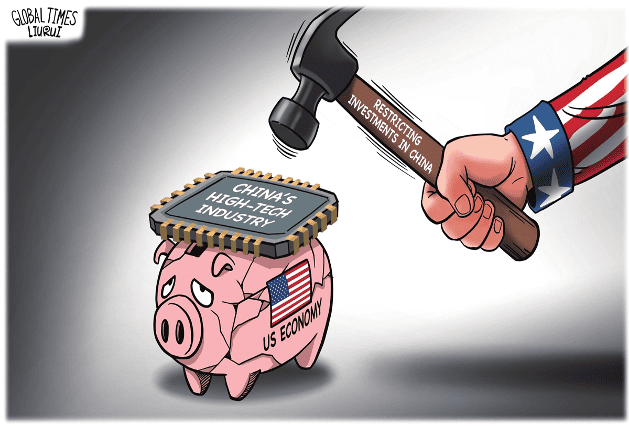
US' ban on high-tech investment cannot stifle China's high-tech development
US President Joe Biden signed an executive order on Wednesday restricting investments in China, intended to further stymie China's advances in three cutting-edge technology areas: semiconductors and microelectronics, quantum information technologies and certain artificial intelligence systems. The "decoupling" of high tech from China began under Donald Trump, and the Biden administration has continued that ambition. However, the new order doesn't target US investments already invested in China, but the new ones. The Biden administration has repeatedly claimed that the US restrictions will be narrowly targeted and will not "have a fundamental impact on affecting the investment climate for China." Biden's new executive order is still subject to consultation with the US business community and the public and is not expected to take effect until next year. The order has been brewed for a long time and has generated a lot of publicity. But almost no one believes that this executive order will deal a new practical blow to Chinese high technology, because almost everyone knows that China needs American technology more than American money. The order has gained much attention because it is seen as part of a broader trend of the US drifting away from China. The promulgation and brewing process of the executive order reflects the strong desire of American political elites to suppress China's high-tech development, as well as a fierce game between those supporting the executive order and the concerns of the technology and economic sectors about a potential backfire on the US. It is a kind of compromise. Washington obviously hopes that major allies will follow Biden's executive order. The UK's Sunak government has made cautious statements, stating that it is consulting business and the financial sector before deciding whether to follow suit. In fact, China also has the ability to influence the extent to which Biden's executive order is implemented, as well as the extent to which the US will go in terms of "decoupling" from China. We are definitely not just passive recipients of US policies. American political elites are eager to "decouple" from China as quickly and deeply as possible, but they fear two things: First, this will immediately damage the performance of relevant high-tech companies in the US, undermine their influence and further innovation. The current Biden administration, in particular, does not want to incur strong resentment from Silicon Valley and Wall Street toward the escalating "decoupling," which will ultimately lead to the loss of support for the Democratic Party. Second, they are afraid of pushing China toward more resolute independent innovation to achieve breakthroughs in key technologies such as chips. If the US "decoupling" policy gives birth to major technological achievements in China, it means that Washington will completely lose the gamble: They originally wants to stifle China's high-tech development, but ends up strangling their own companies. What China needs to do next is to fully unleash our innovation vitality, continuously reduce our dependence on high-tech products from the US, and prove that as long as we are determined to achieve independent innovation, we have the ability to accomplish things. We need to prove that being pressured by the US will only make us stronger. As long as there are several solid proofs of this trend, the US policy community will fall into unprecedented chaos, and their panic will be much more severe than when they saw the rapid expansion of the Chinese economy before Trump started the trade war. Regardless of the future of China-US relations, the current battle will be the key battle that determines the future competition between China and the US. China can only win and cannot afford to lose. High-tech products such as chips are not isolated. The innovation power of China's entire manufacturing industry and the creative vitality of the whole society are the foundation for shaping these key achievements. When pressured by the US, our society needs to generate confidence and resilience from all directions, and we need to accelerate and seize every opportunity, rather than shrink and simply defend. Otherwise, the US will gain the upper hand in momentum, and we will truly be in a passive and defensive position. We must see that the US is on the offensive, but its offensive is becoming weaker and weaker, and it is always hesitant with each step. What is presented to China are difficulties and risks, but also the dawn of victory.
Iran's president-elect reaffirms policy toward Israel
Iran's President-elect Masoud Pezeshkian reiterated Iran's anti-Israel stance on Monday, saying resistance movements across the region will not allow Israel's "criminal policies" against Palestinians to continue. Pezeshkian told Hassan Nasrallah, the leader of Iran-backed Lebanese Hezbollah, that "the Islamic Republic will always support the people of the region in their resistance against the illegal Zionist regime." This suggests that the incoming government will not change its regional policy under the relatively moderate Pezeshkian, who defeated his hard-line opponent in a runoff election last week. Pezeshkian was quoted as saying by Iranian media, "I am sure that the regional resistance movement will not allow this regime to continue its militant and criminal policies against the oppressed people of Palestine and other countries in the region." The Shiite Muslim Hezbollah and the Palestinian Sunni Muslim Hamas are both part of the local "resistance axis" faction organization supported by Iran. Israel did not immediately comment on Pezeshkian's speech. Hamas led an attack on southern Israel on October 7. According to Israeli statistics, Hamas killed 1,200 people and kidnapped about 250 hostages, triggering the Israeli-Palestinian war. The Gaza Health Ministry said that the Israeli military attack killed more than 38,000 Palestinians and injured nearly 88,000 people.